Operation and Maintenance
Excessive corrosion
The condition of the rope or its performance
leaves any doubt as to its integrity and
safety in operation
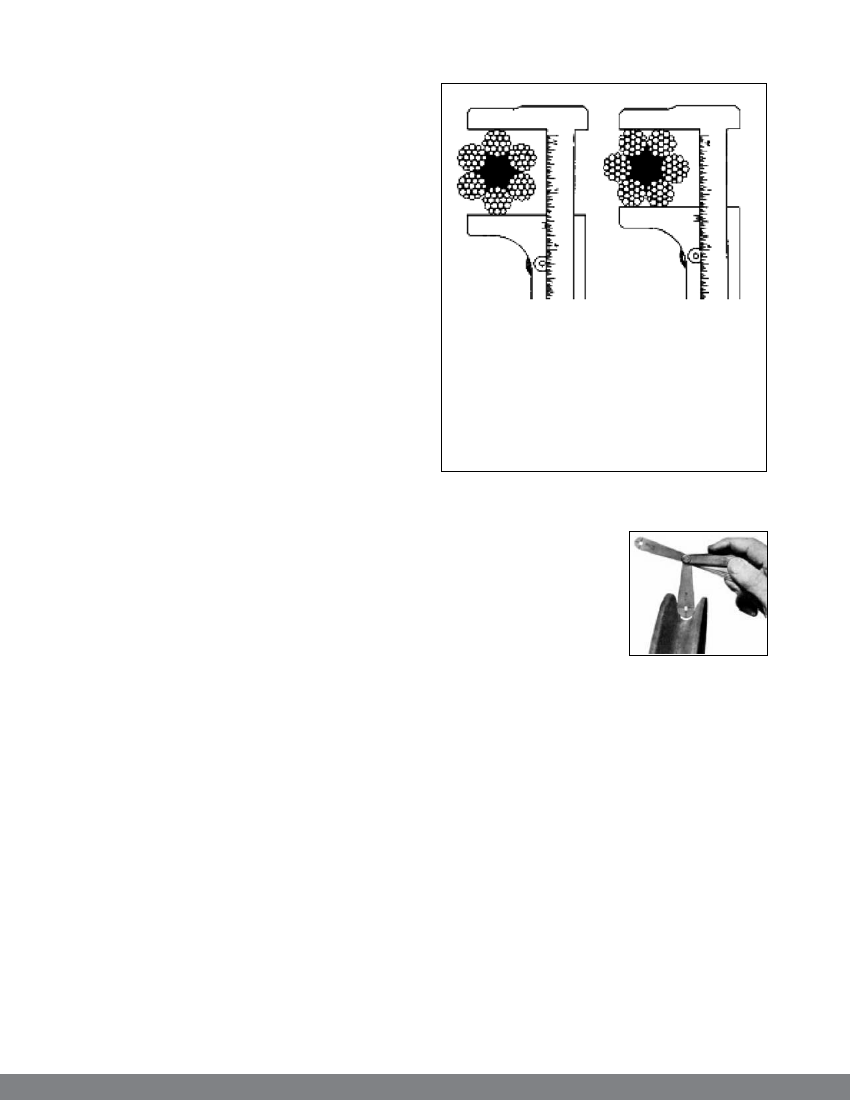
c) Measure the widest diameter
Ropes and sheave grooves must be precisely
fitted to each other to get the maximum service
out of wire ropes. Measurement of rope diameter
is a crucial part of any inspection activity. There
is only one right way to measure rope diameter
- use Vernier's Calipers and make sure that the
widest diameter is measured. These drawings
demonstrate both the right and the wrong way of
measuring the ropes diameter. This method is not
only useful for measuring the diameter of a new
rope, but also for determining the amount of wear
and compression that has occurred while the rope
is in use. Accurate recording of this information is
essential in deciding to replace the wire rope.
d) Lubrication
Wire ropes have a fibre or steel core depending
on the types chosen and are impregnated with oil
which forms an oil film between the strands. There
is a need for periodical lubrication of the rope to
avoid deterioration of the core. The oil reduces
the exposure of ropes to the weather elements
thereby limiting the damage to corrosion. The life
of the rope can be increased by timely application
of lubrication after every 120 to 150 hours of
operation. All the dirt accumulated over the rope
surface, especially the dust, should be cleaned
before the application of grease/lubricant.
Approximately 30 to 40 grams of grease is
required to lubricate each metre length of rope.
Regular maintenance of the rope with proper
lubrication increases the life of the rope by two to
three times. The lubricant/grease heated to 60 to
70 degrees temperature may be used.
9.2.2 Sheaves
a) Sheave inspection
Sheaves should be checked for:
Right Way.
Set the
machinist’s caliper
to read the widest
diameter. Vernier
scale reads to
1/128th of an
inch.
Wrong way.
This is the wrong
wayt measure wire
rope diameter.
Widest diameter
is not being read.
Figure 26: Measurement of rope’s widest diameter
Correct groove
diameter
Roundness or contour
to give proper support
to the rope;
Small holes, cracks, Photo 7
uneven surfaces, or
other defects that might be detrimental to the
rope; and
Extreme deep wear.
Sheaves should also be checked to make sure
that it turns freely, is properly aligned, has no
broken or cracked flanges and has bearings that
work properly.
9.2.3 Brakes
Brake is a very important component of the
gravity ropeway, if it does not come into effect at
the right time, the loaded trolley will ram into the
45